Medicine
Medicine has to do with diseases and conditions that affect the entire body. In this section, learn about testing and treatment plans including the medicines used to prevent and treat a range of diseases and conditions.

Is Your Hospital Diverting Ambulances Because of COVID-19?

How Ambulances Work

Can You Go to the ER Without Health Insurance?
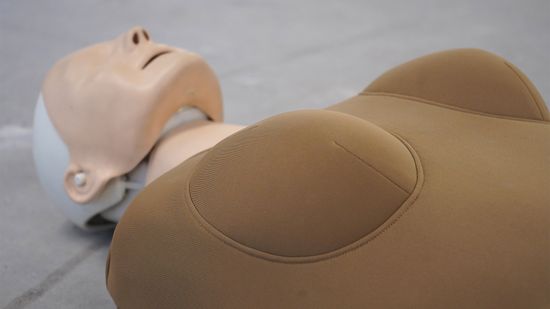
Womanikin: Overcoming the Stigma of Breasts and CPR

Women Less Likely to Receive CPR in Public, Study Finds
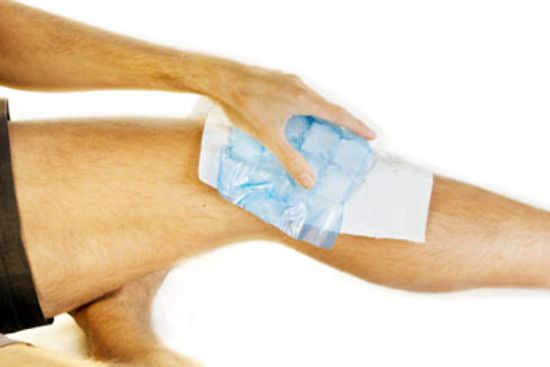
Should you use ice or heat to treat an injury?
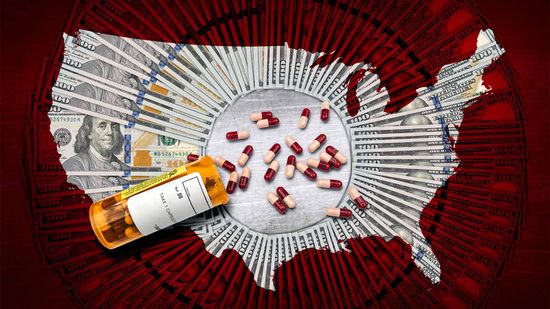
Mark Cuban Wants to Solve the U.S. Prescription Drug Price Crisis

Epidemiologists Are the 'Disease Detectives' Protecting Public Health

Should Doctors Have to Pay Patients for Running Late?

FDA Approves OTC Narcan Nasal Spray for Opioid Overdose

Why Are Potassium Iodide Pills Selling Like Crazy?
Why Are Some Shots Given in the Arm and Some in the Bum?

Medical Schools Have Come a Long Way From Grave Robbing to Get Cadavers

Compression Wear Is Key to Sports and Surgical Recovery

How Doctor On Demand Works
Anesthesia Awareness: When You're 'Awake and Aware' During Surgery

Prehab Could Make Your Recovery From Surgery a Bit Easier

You Need It Like a Hole in the Head: The Ancient Medical Art of Trepanation

Honey Can Help If Your Child Swallows a Button Battery

What Is the Rarest Personality Type?
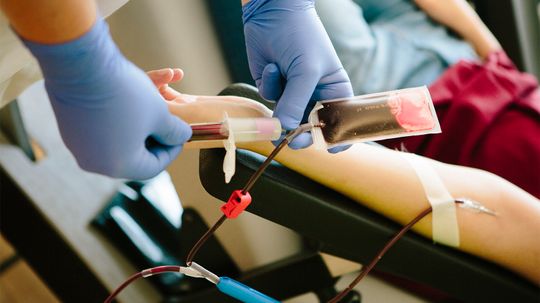
Veins, Needles, Yikes: What to Know Before Having Blood Drawn
Are Army medics and doctors on the front lines?
Can civilians become doctors in the U.S. Army?

Do Army doctors and medics carry weapons?
Learn More / Page 2
Having blood drawn is a piece of cake for some people and a traumatic experience for others. Either way, being armed with information can only help make the process easier.
When you call 911 in the U.S., you expect an ambulance to come roaring to your aid in a matter of minutes. But how are ambulances dispatched — and why do they cost so much?
Making sure the bowels are moving is key to monitoring health after surgery.
Advertisement
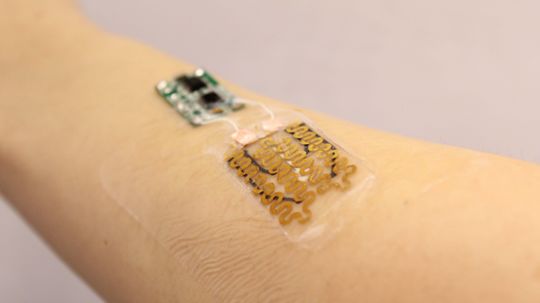
Flexible electronics have enabled a team at Tufts University to create a bandage that not only monitors wounds, but delivers treatment as well.
The intent of Right to Try is to make the process of obtaining last-ditch, potentially life-saving drugs easier for terminally ill patients by avoiding FDA strictures altogether.
By Carrie Tatro
Not all drugs are created equal. And not all drugs are prescribed for the particular conditions they're technically approved to treat, either. That's when they fall into the off-label category, and they're more common than you think.
Hearing loss due to loud noise or certain medicines is irreversible, but soon we might be able to prevent hearing loss before it begins.
Advertisement
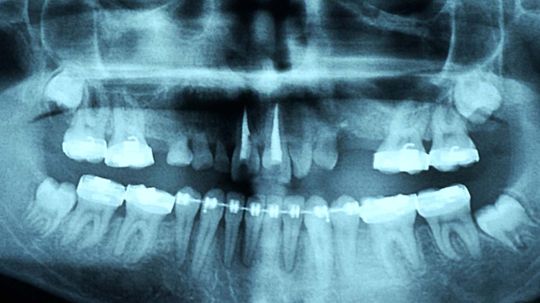
What happens when permanent teeth don't come in behind our baby teeth? Turns out there are treatments, but they'll cost you (both time and money).
Is microdosing LSD just a silly fad or is it time to take a comprehensive look at its potential benefits?
By Jamie Allen
Lots of factors can affect a bystander's decision to perform CPR, and a big one seems to be gender.
By Robert Lamb
Psilocybin (the drug in magic mushrooms) provides relief for severely depressed people, according to new research. But there are some caveats.
By Alia Hoyt
Advertisement
There's a good chance you've taken a personality test, and can now officially claim your type. But how valid are these assessments, and why do we even take them in the first place?
The strong and sticky goo of the Dusky Arion slug provided scientists with unlikely inspiration for a glue that sticks well to wet surfaces.
A single vial of snakebite antivenom can run thousands of dollars. Why? It actually has little to do with the production process.
A new study found gifts from pharmaceutical reps could be influencing the prescribing behavior of doctors.
By Alia Hoyt
Advertisement
A huge number of clinical trials — many of which are testing life-saving drugs — languish due to low participation levels. Why is that, and what can be done?
By Alia Hoyt
A series of papers showed that overuse and underuse of medical care is a global health crisis. Here's how to address it.
By Alia Hoyt
This new study could present alternative to drugs with negative side effects. And parents of pre-surgery children experience less anxiety, too.
Although several states have proposed legal action banning the question, only Florida has actually passed a controversial law addressing the issue.
Advertisement
You won't believe some of the emergency medical procedures people have performed under duress. They range from sucking out venom to performing a Caesarean birth. Could you do the same?
The current U.S. recommendation is to get a tetanus shot every 10 years. Will this new study change CDC guidelines?
By Alia Hoyt
Docs are no different from the rest of us — they bring their unconscious biases into the workplace. But is there a way to lessen the impact of these biases on patients?
By Alia Hoyt
It may sound crazy initially — using a tooth to repair eyesight — but it's a very real surgery with a pretty impressive track record.
Advertisement
Bee stings hurt, so it seems like an odd proposition to get them on purpose. Believe it or not, the venom that makes that sting may also benefit humans in therapy.
You really liked that ER doctor who stitched up your arm. That is until you got your bill. Turns out the doctor was out of your insurance network, even though the hospital's ER is in network. How does that happen?