Genetic Science
Genetics is the study of cellular science. It furthers our understanding of how DNA and the genetic make-up of species and can lead to cures for diseases and shape our future.

Why do people sing in the shower?

10 Bizarre Treatments Doctors Used to Think Were Legit

Ancient Egyptian Pregnancy Test Survived Millennia Because It Worked

Can You Crack This Nuts Quiz?

The Science Behind Your Cat's Catnip Craze

Corpse Flower: When Nature Deceives

Hypertonic vs. Hypotonic Solutions: Differences and Uses

Your Phone Is a Germ Factory, So Stop Taking It to the Toilet

Why Even Identical Twins Have Different Fingerprints

Howstuffworks Interviews: Extinction Level Events with Annalee Newitz

What will the Earth look like in 50,000 years?

How did language evolve?

Differences Between Pet Training and Animal Conditioning

What Is Shadow Work and How Does It, Well, Work?

Why can't we remember being babies?
Learn More
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the average height in the United States is 5 feet, 9 inches (1.75 meters) for adult men and 5 feet, 3.5 inches (1.61 meters) for adult women. But some people can reach heights upwards of 7 or 8 feet (2.1 to 2.4 meters)!
By Sascha Bos
Before the widespread use of DNA, establishing the paternity of a child was a tricky business. Ever heard of the oscillophore?
By Dave Roos
After scientists announced the first draft of the human genome, people began to wonder how our new understanding of DNA would change life. Several research institutes stated the accomplishment would revolutionize science and modern medicine -- but how, exactly?
Advertisement
What's more fun than looking at pictures of DNA and celebrities? Check out Dolly, dimples and dominant and recessive traits in this fun gallery charting how genetics play out in humans (and a few animals).
How can children from the same parents look so different? I mean, why don't all kids from the same parents look exactly alike, since the parents just have one set of chromosomes each and they don't change?
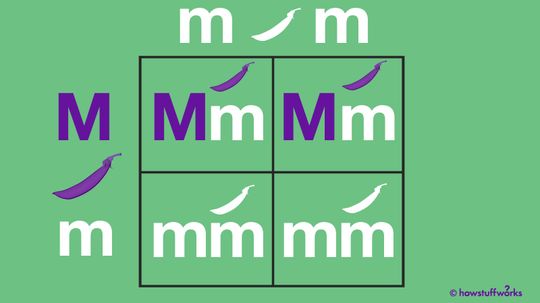
A Punnett square helps predict the possible ways an organism will express certain genetic traits, such as purple flowers or blue eyes.
CRISPR is the genius behind innovations that seemed impossible a decade ago. Could you grow tomatoes with the kick of hot sauce or ferment wine that doesn't cause a hangover? That's just two of the things scientists are looking into.
Advertisement
We love stories of twins who can sense each other's pain or know what the other is thinking. But is there really such a thing as "twinspiration" or is just coincidence?
Genetic mutations are the instrument by which nature adds new variations to life. If the mutations give rise to advantageous traits, they get passed down through successive generations and can spread throughout the entire population of a species. Evolution just wouldn’t be possible without mutations springing up now and again to bestow new attributes on […] The post 8 Super Cool Genetic Mutations Found In Humans appeared first on Goliath.
By Wes Walcott
You probably feel like you have very little in common with that banana lying on your kitchen counter. But science says you do! So, how is this possible? And is that stat accurate? We talk to the scientist who did the research.
By Alia Hoyt
It's one of those words that might remind you of certain gender-bending musicians from the '80s, but what does it mean today?
Advertisement
At least two commercial DNA testing services offer users information on heritage coming from coupling between ancient humans and other species.
A groundbreaking study finds light skin pigmentation gene variations originating in Africa, eroding the notion of race as a biological characteristic, and shedding light on cancer and evolution, too.
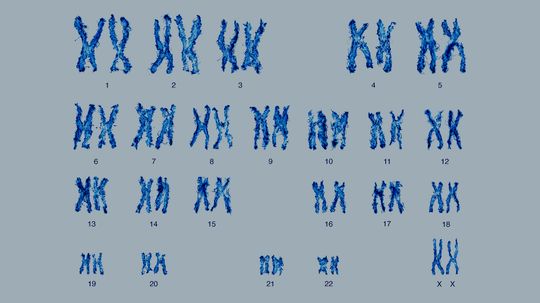
Nearly every living cell is made of DNA, and every chromosome contains exactly one molecule of DNA. But not all cells are made of the same number of chromosomes.
Humans are a diverse lot — which is good! The question of ethnicity vs. race vs. nationality is a source of much debate, even among experts.
By John Donovan
Advertisement
Cell division can be confusing, but it's not as difficult if you pretend chromosomes are sentences.
The real story about the roots of infidelity and monogamy is far more complicated than whether you have the "cheating gene."
By Dave Roos
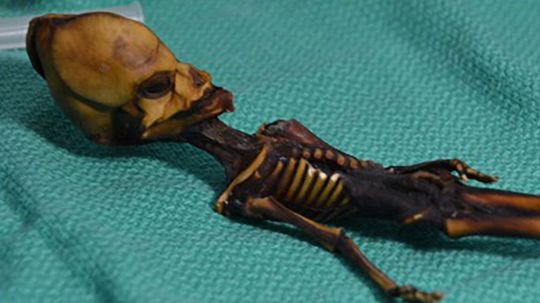
The Atacama skeleton has sparked intense controversy and, based on its appearance, speculation of alien origin since its discovery in 2003. But what is the real story behind this little skeleton?
By Mark Mancini
Tetragametic chimerism occurs when a single organism has two genetically distinct types of DNA.
Advertisement
Does everyone have a double out there somewhere that they don't know about? Science says the odds are pretty slim.
By Alia Hoyt
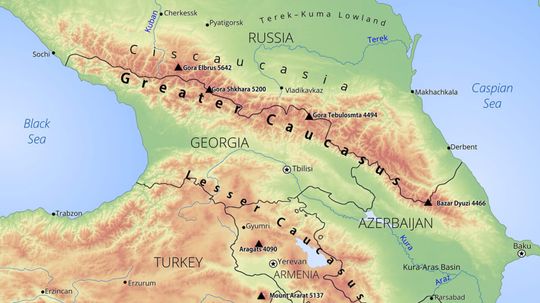
It's easy to equate Caucasian with white. But the word Caucasian touches on issues deeper than skin color. HowStuffWorks looks at its true meaning.
What happens when twins are reunited decades later? And how in the world can you explain separated twins giving their firstborn son or their family dog the same exact name?
By John Donovan
Is it better to be grossed out by the smell of your asparagus pee, or not to be able to smell it all? A new study explains why some of us can detect this unique odor.
Advertisement
Scientists are discovering why some people break out into hives from physical contact like clapping hands or running.
Countless superhero movies have been released in the past decade, playing to our fascination with people with higher than usual abilities. But what if people really could have superpowers like those portrayed in the movies, thanks to the inheritance of so-called super genes?
By Diana Brown & Sascha Bos