A little more than half of the adults in the United States are overweight. Statistics show that an incredible 65.2 percent of the U.S. population is considered to be "overweight" or "obese." According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), obesity and overweight status is determined in adults by finding a person's "Body Mass Index" or BMI.
BMI is a calculation that takes into consideration both a person's body weight and height to determine whether they are underweight, overweight or at a healthy weight. An adult who is considered "overweight" has a BMI somewhere between 25 and 29.9. An adult with a BMI of at least 30 is considered "obese." This measurement is used because it's typically a good indicator of body fat.
Advertisement
Whether due to concern for related health risks (high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, sleep apnea, respiratory problems, etc.), or just for sheer aesthetics, many Americans worry about fat. In fact, at this very moment, thousands of Americans are exercising or dieting to reduce their amount of body fat. But have you ever wondered what fat is? When a person "gets fat" -- gains weight -- what is actually happening inside the person's body? What are "fat cells" and how do they work?
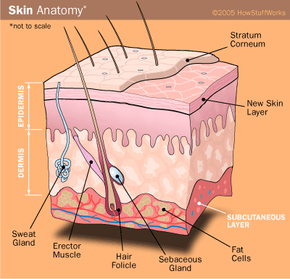
Fat, or adipose tissue, is found in several places in your body. Generally, fat is found underneath your skin (subcutaneous fat). There's also some on top of each of your kidneys. In addition to fat tissue, some fat is stored in the liver, and an even smaller amount in muscle.
Where fat is concentrated in your body depends upon whet her you are a man or woman:
- An adult man tends to carry body fat in his chest, abdomen and buttocks, producing an "apple" shape.
- An adult woman tends to carry fat in her breasts, hips, waist and buttocks, creating a "pear" shape.
The difference in fat location comes from the sex hormones estrogen and testosterone. Fat cells are formed in the developing fetus during the third trimester of pregnancy, and later at the onset of puberty, when the sex hormones "kick in." It is during puberty that the differences in fat distribution between men and women begin to take form. One amazing fact is that fat cells generally do not generate after puberty -- as your body stores more fat, the number of fat cells remains the same. Each fat cell simply gets bigger! (There are two exceptions: the body might produce more fat cells if an adult gains a significant amount of weight or has liposuction performed.)
In this article, we will look at how fat cells store fat and how they get rid of it. See the next page to learn more.