Blood Flow
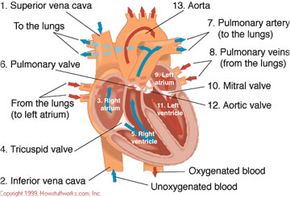
All blood enters the right side of the heart through two veins: The superior vena cava (SVC) and the inferior vena cava (IVC) (see figure 3).
The SVC collects blood from the upper half of the body. The IVC collects blood from the lower half of the body. Blood leaves the SVC and the IVC and enters the right atrium (RA) (3).
Advertisement
When the RA contracts, the blood goes through the tricuspid valve (4) and into the right ventricle (RV) (5). When the RV contracts, blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve (6), into the pulmonary artery (PA) (7) and into the lungs where it picks up oxygen.
Why does it happen this way? Because blood returning from the body is relatively poor in oxygen. It needs to be full of oxygen before being returned to the body. So the right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs first to pick up oxygen before going to the left side of the heart where it is returned to the body full of oxygen.
Blood now returns to the heart from the lungs by way of the pulmonary veins (8) and goes into the left atrium (LA) (9). When the LA contracts, blood travels through the mitral valve (10) and into the left ventricle (LV) (11). The LV is a very important chamber that pumps blood through the aortic valve (12) and into the aorta (13). The aorta is the main artery of the body. It receives all the blood that the heart has pumped out and distributes it to the rest of the body. The LV has a thicker muscle than any other heart chamber because it must pump blood to the rest of the body against much higher pressure in the general circulation (blood pressure).
Here is a recap of what we just discussed. Blood from the body flows:
- to the superior and inferior vena cava,
- then to the right atrium
- through the tricuspid valve
- to the right ventricle
- through the pulmonic valve
- to the pulmonary artery
- to the lungs
The blood picks up oxygen in the lungs, and then flows from the lungs:
- to the pulmonary veins
- to the left atrium
- through the mitral valve
- to the left ventricle
- through the aortic valve
- to the aorta
- to the body