Body Systems
Your body is pretty amazing. At any given point you have many biological processes going on -- circulatory, digestive, brain & central nervous systems and more. Learn about these body systems as well as the eye, ears, nose and throat.

Ever Stand Up and Get Dizzy?

How White Matter Helps the Brain's Gray Matter Function

Bruce Willis Has Aphasia. What Is It and What Causes It?

The True Story of the Blue People of Kentucky

What Is the Rarest Blood Type in the World?
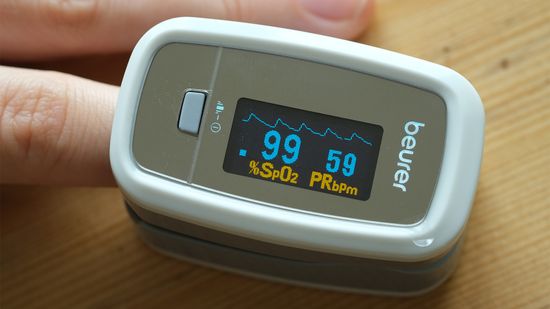
What Does It Mean If Your Blood Oxygen Level Is Low?

What Is Saliva and How Does It Change the Taste of Food?

The World's Longest Poop Story Is a Crock of, Well ...

When You Have to Go But Don't Want People to Know

Does Oxytocin Make Us Fall in Love?

5 Ways Homeostasis Keeps Your Body Humming Along

Is It Possible to Get Taller as an Adult?

Do You Have One of the 6 Rarest Eye Colors in the World?

Why Do Babies' Eyes Change Color?

There Are 6 Different Eye Shapes. Which One Is Yours?

'Man Flu' Could Be a Real Thing

Sugars in Human Breast Milk Act as Antibacterial Agents

Does mouthwash affect your immune system?

Kidney Stones Are Excruciating, But the Source of Pain Is Surprising

Why Do We Do a Little Dance When We Have to Pee?

Do You Turn the Door Key and Have to Pee? It May Be All in Your Brain
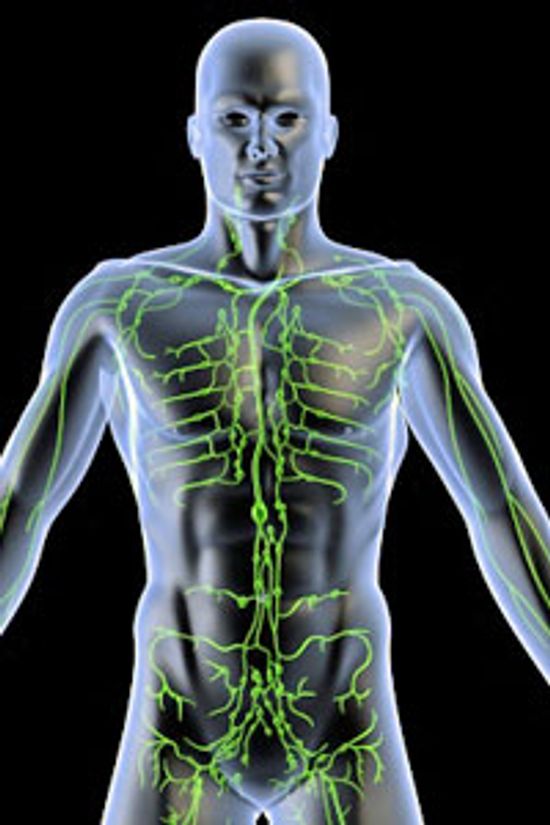
The Lymph System
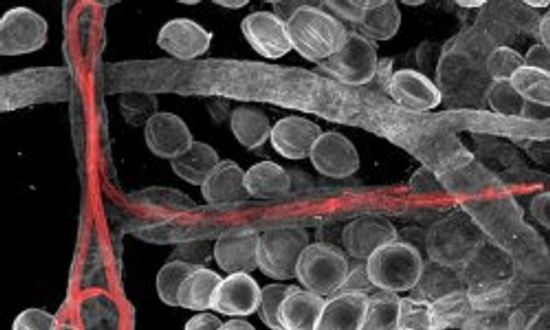
What is lymph?
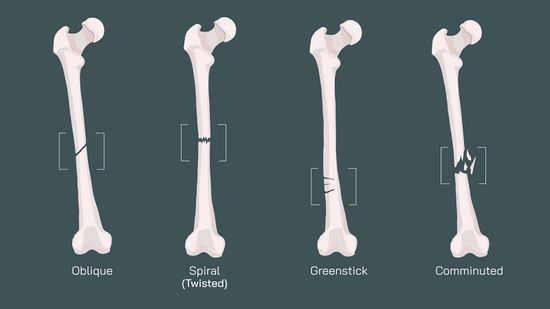
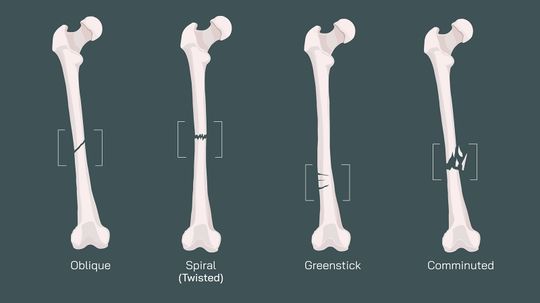
11 Types of fractures That Can Show Up in an X-ray or MRI

How One Key Protein May Help Tendons Enhance Athletic Performance

What Are Muscle 'Knots' and How Do You Get Rid of Them?

What Happens When the Wind Is Knocked Out of You?

The Science Behind Why We All Have Snot

Why Breathing Through Your Nose Is Best
Learn More
A bone fracture can happen in an instant—from a fall, an accident, or even repetitive stress. But not all fractures are the same. Understanding the different types of fractures can help you grasp how bone breaks occur, how they’re diagnosed, and what the healing process might involve.
Some bodily phenomena make sense. An ice cream headache, for example - you know what you did to get there, you know you deserved it, and you have absolutely no regrets. Others are a bit of a mystery, like when you stand up quickly and see a dizzying array of stars.
All eye colors are an interaction of brown pigment and light, but some eye colors occur much less often than others. Here are the six you'll see the least.
Advertisement
Surely you've had the wind knocked out of you at some point in your life. But what's really going on inside your body?
Saliva is not exactly the most appetizing of subjects, but it plays an important role in everything from how food tastes to how it is digested.
The presence of a protein called Piezo1 plays a key role in how tendons heal - and a genetic mutation in that protein may also enhance athletic performance and keep us moving around longer and better.
Believe it or snot, almost every living creature has some kind of mucus - because mucus does so many things. A study found mucus was so beneficial to mammals, it evolved independently in species.
Advertisement
Surely you've had a knot in your neck at some point. But your muscles really aren't tied in knots. Or are they?
Having kidney stones can feel like you've been stabbed in the back. But is it the stones causing the searing pain or is it something else?
By Dave Roos
We've all heard of the brain's gray matter, but what about the white matter? What does it do?
The director of the Aphasia Research Laboratory at Boston University explains the condition forcing Bruce Willis to retire from acting, including what treatment options could be available.
By Swathi Kiran
Advertisement
Maybe you've seen those fantastical stories saying the world's longest piece of poop is 26 feet? Is that even possible? Where does crap like this come from?
By Alia Hoyt
Many things play a role in how our bodies acclimate to super-cold temperatures, including our own habits, genetics and even brown fat.
Nearly all newborns have some shade of blue eyes at birth. But after a few months, they change. What's going on?
Knowing your eye shape can help with everything from selecting eyeglass frames to shaping the perfect brow.
Advertisement
The Fugate and the Combs families in rural Kentucky lost the genetic lottery, as both shared a rare recessive trait that made their skin look blue. What happened to the blue people of Kentucky?
By Dave Roos
Stanford researchers have developed a new white cane, incorporating sensing and wayfinding approaches from robotics and self-driving vehicles. Could this new white cane reshape life for the visually impaired?
Parosmia is a post-COVID-19 side effect that distorts your sense of taste and smell. But smell training (you read that right) can help most people get things back on track.
Technology for hearing aids has advanced drastically since our grandparents wore those big, bulky ones wrapped around their ears. Now they're Bluetooth-enabled and can even translate foreign languages on the fly.
Advertisement
Does using a bathroom other than your own freak you out? The Faux Fan drowns out the sounds your body makes when you have to, well, go, so you can poop without worrying people will hear.
By Meg Sparwath
Empty nose syndrome is a rare problem where patients have clear nasal passages but constant sensations of being unable to breathe. And worst of all, many doctors believe it's all in their heads.
Savant syndrome is a rare condition in which someone with significant mental disabilities demonstrates certain unexplained extraordinary abilities, such as playing music or remembering prodigious amounts of information.
We've probably all been breathing wrong our entire lives. Why is that? Experts suggest we should focus on breathing through our noses and most of us don't.
Advertisement
There are eight major blood types and some are more common than others. But what's the rarest of them all?
Proprioception refers to our ability to perceive our body's position and how we move through space. It's often considered our sixth sense because we do it without thinking about it.