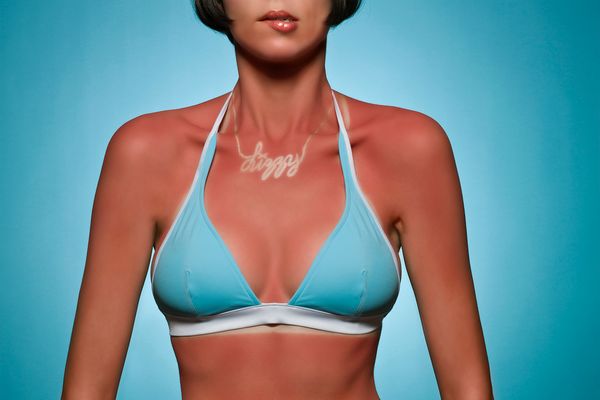
When your skin is exposed to the sun's rays, it absorbs the radiation that light carries with it. Sunlight that reaches us here on Earth consists of ultraviolet (UV) A and B radiation. UVA waves account for about 95 percent of the sun's radiation on the planet. It has the longest wavelength of the sun's UV rays and can penetrate the protective outer epidermal layers to the dermis, where new skin cells are created. UVB rays are generally absorbed by the epidermal layers.
Although UVB radiation is more potent than UVA radiation, it doesn't penetrate as deeply. What's more, it also reflects easily off surfaces like snow or metal, allowing it to be absorbed by the skin twice. Once they penetrate the skin, researchers believe both UVA and UVB radiation alter the DNA of the skin cells they touch, which leads to skin cancer. These mutations affect cell functioning and controlled growth among skin cells, which can cause tumors.
Advertisement
Both UVA and UVB radiation also create another reaction in skin layers, melanin production. Melanocytes, or melanin-producing skin cells, increase the production of melanin when the skin is assaulted by UV rays. This pigment is responsible for tanned skin, but its role is to absorb and diffuse UVA and UVB radiation on the cellular level.
Melanin can't absorb all radiation that penetrates skin, however, and eventually another process takes over -- sunburn. Within a few hours of overexposure to the sun's rays, sunburned skin will become reddish, painful, warm and swollen. Blisters may form and bad enough sunburn can also trigger headaches and nausea.
As sunburns heal, another standard characteristic emerges: dry, flaky skin. Some of the best home remedies to treat sunburn are moisturizers. But with painful and inflamed skin, exactly how should you keep your sunburn moisturized? Read the next page to find out.
Advertisement