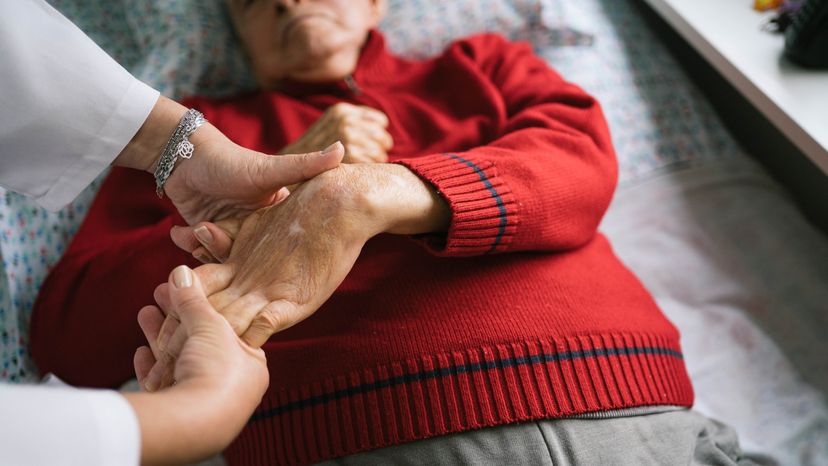
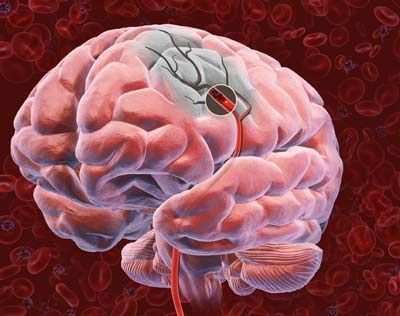
Some stroke patients find themselves suffering from frequent or nonstop bouts of the hiccups after their stroke. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. An ischemic stroke happens when an artery becomes blocked and not enough blood can reach your brain. They're the most common types of strokes. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel in your brain leaks or bursts. Meanwhile, hiccups are a temporary movement disorder that involves your brain, spinal cord, nerves and muscles. They happen when your diaphragm spasms and your glottis suddenly closes, causing a noisy sound. If a stroke disrupts the breathing center in your brain, you can end up with hiccups.
While time is typically the best cure for hiccups, recovering stroke patients are sometimes prescribed chlorpromazine or baclofen to treat their constant hiccups. When hiccups caused by a stroke don't go away, the cause of the hiccups has to be located and corrected.
Advertisement