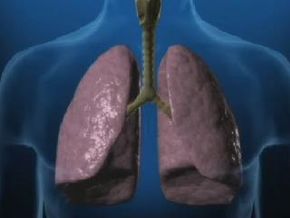
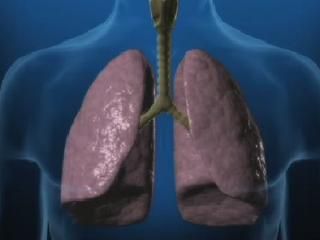
Emphysema is an irreversible condition in which air becomes trapped in the lungs, making it difficult to exhale. Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and the most common cause is smoking. Emphysema occurs when the tiny air sacs in the lungs, through which oxygen is transferred to the body, are damaged and eventually destroyed. The air sacs, called alveoli, are normally spherical in shape; as they're damaged, they take on irregular shapes and develop big holes in their inner walls. The walls of the alveoli are where oxygen transfer takes place, and when they are damaged, oxygen is no longer able to enter into your blood stream.
In addition, the damaged alveoli, called “blebs,” lose the elastic fibers that are required to hold open the alveoli so air can come out of the lungs when you exhale. Instead, the blebs collapse and trap air inside them, preventing you from breathing out. This also reduces the volume of air that your lungs can hold since the blebs are taking up lung space with trapped air; this means you won’t be able to breathe in enough oxygenated air to function properly. So if you have emphysema, you'll feel breathless and have a chronic cough as a result of the airway inflammation. You may also experience chest tightness, loss of appetite and fatigue.
Advertisement
Treatment for emphysema helps to slow the process of airway destruction but cannot reverse it. Treatment commonly involves inhalers to open the airways, supplemental oxygen and other medications, including steroids, antibiotics or reflux medications. A pulmonary rehabilitation program can help you to stay active and will provide you with education on how to live with emphysema.