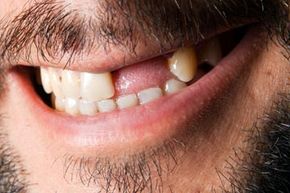
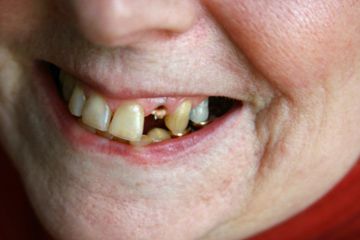
When you were a kid, tooth loss meant a financial reward from a benevolent, mythological creature. The event also enhanced the charm of your smile, drawing many "oohs" and "aahs" from grown-ups. As an adult, however, you shouldn't expect such results. Not only can tooth loss lead to costly dental treatments, it can also detract from your physical appearance. And the disadvantages don't end there; tooth loss can actually increase your risk of getting serious, chronic illnesses. But before we cover those diseases, let's look at the primary one that's responsible for tooth loss in the first place: periodontal disease.
Periodontal disease, aka gum disease, is not the only cause of tooth loss, but it's the primary reason people over age 35 lose their teeth [source: American Academy of Periodontology]. Less common sources of tooth loss include osteoporosis and injury to the face. Osteoporosis is a culprit because a reduction in bone density can lead to deterioration of the bone that supports the teeth [source: American Academy of Periodontology].
Advertisement
When it comes to periodontal disease, there are two phases: gingivitis, which causes painful, bleeding and swollen gums, and periodontitis, the advanced stage. However, the condition first starts with plaque, that sticky material that clings to teeth and gums. Plaque is filled with bacteria, and that bacteria creates acids and chemicals that break down gum tissue.
Plaque is a naturally occurring substance in the mouth, so it can't be completely prevented. It is, however, possible to reduce the presence of this gum destroyer with proper oral hygiene, which includes brushing, flossing and visits to your dentist for cleanings and checkups on a regular basis. Conditions and habits that can make plaque harder to control include smoking, chewing tobacco, family history of gum disease, stress, low-nutrient diets and a weakened immune system caused by diabetes, leukemia or AIDS.
We've covered the main disease that causes tooth loss, now let's look at how it can lead to other diseases and conditions. Keep reading to learn more.
Advertisement