"What's in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as sweet."
A name may be nothing but an artificial convention in William Shakespeare's eyes, but when it comes to describing a medical condition, sometimes the name says it all. Take Jumping Frenchmen Disorder, for example. Most people have never heard of this rare ailment that affects a person's automatic response system, but they wouldn't be surprised to learn its symptoms include an exaggerated startle or jump reflex [source: WebMD].
Advertisement
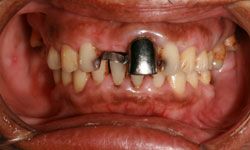
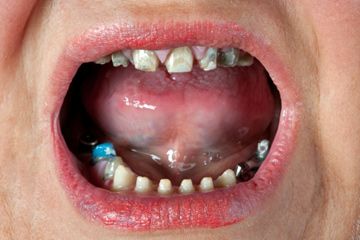
Likewise, one doesn't necessarily need to know exactly what trench mouth is to be fairly certain it's not a good thing. Formally known as Vincent's stomatitis and necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis -- but nicknamed trench mouth because of its prevalence among World War I soldiers who were stuck in the trenches without the means to take care of their teeth -- trench mouth is the uglier, lesser known cousin of oral infections like gingivitis and periodontitis [source: Mayo Clinic].
Nowadays, trench mouth is rare throughout most of the world, but it remains common among teenagers and young adults in developing countries where people suffer from poor nutrition and inadequate living conditions [source: Mayo Clinic].
Read on to learn about the symptoms of trench mouth.
Advertisement