Consider this. You touch a hot object and immediately drop it or withdraw your hand from the heat source. You do this so quickly you don't even think about it. How does this happen? Your nervous system coordinated everything. It sensed the hot object and signaled your muscles to let it go. Your nervous system, which consists of your brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves and autonomic nerves, coordinates all movements, thoughts and sensations that you have. In this article, we'll examine the structure and functions of your nervous system, how nerve cells communicate with each other and various tissues and what can go wrong when nerves become damaged or diseased.
The nervous system:
Advertisement
- Senses your external and internal surroundings
- Communicates information between your brain and spinal cord and other tissues
- Coordinates voluntary movements
- Coordinates and regulates involuntary functions like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature.
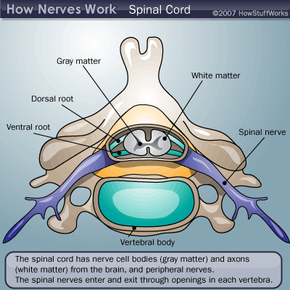
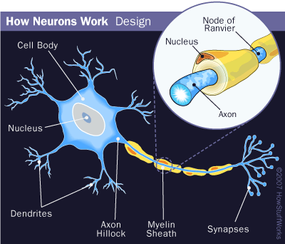
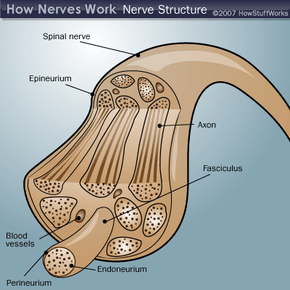
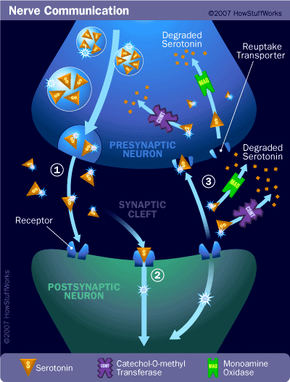
The brain is the center of the nervous system, like the microprocessor in a computer. The spinal cord and nerves are the connections, like the gates and wires in the computer. Nerves carry electrochemical signals to and from different areas of the nervous system as well as between the nervous system and other tissues and organs. Nerves are divided into four classes:
- Cranial nerves connect your sense organs (eyes, ears, nose, mouth) to your brain
- Central nerves connect areas within the brain and spinal cord
- Peripheral nerves connect the spinal cord with your limbs
- Autonomic nerves connect the brain and spinal cord with your organs (heart, stomach, intestines, blood vessels, etc.)
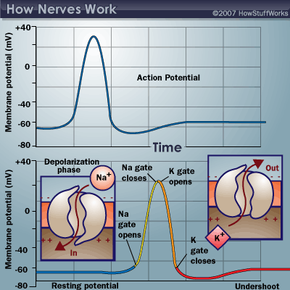
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, including cranial and central nerves. The peripheral nervous system consists of the peripheral nerves, and the autonomic nervous system is made of autonomic nerves. Fast reflexes, like removing your hand quickly from a heat source, involve peripheral nerves and the spinal cord. Thought processes and autonomic regulation of your organs involve various parts of the brain and are relayed to the muscles and organs through the spinal cord and peripheral/autonomic nerves.
Advertisement