Medicine
Medicine has to do with diseases and conditions that affect the entire body. In this section, learn about testing and treatment plans including the medicines used to prevent and treat a range of diseases and conditions.

Is Your Hospital Diverting Ambulances Because of COVID-19?

How Ambulances Work

Can You Go to the ER Without Health Insurance?
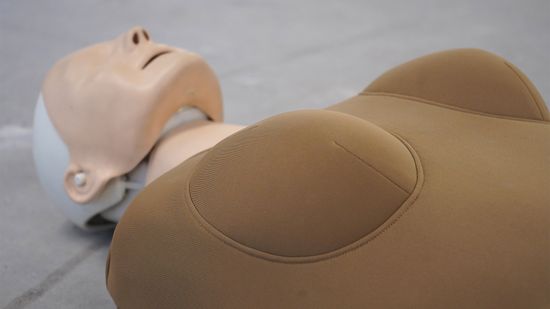
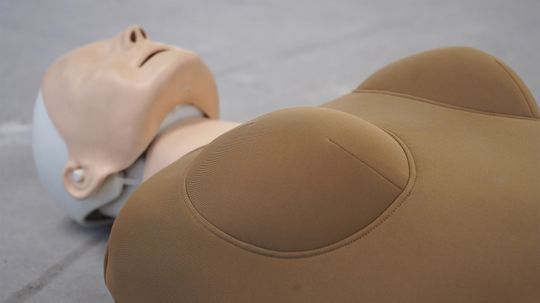
Womanikin: Overcoming the Stigma of Breasts and CPR

Women Less Likely to Receive CPR in Public, Study Finds
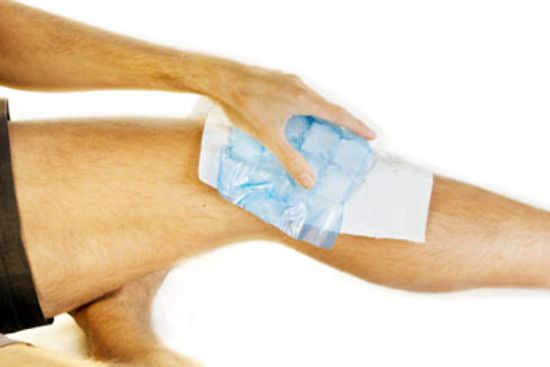
Should you use ice or heat to treat an injury?
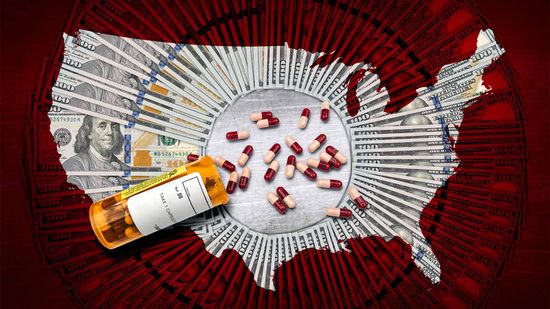
Mark Cuban Wants to Solve the U.S. Prescription Drug Price Crisis

Epidemiologists Are the 'Disease Detectives' Protecting Public Health

Should Doctors Have to Pay Patients for Running Late?

Thalidomide: How a Miracle Medication Became a Global Tragedy

FDA Approves OTC Narcan Nasal Spray for Opioid Overdose

Why Are Potassium Iodide Pills Selling Like Crazy?

Who's the Most Powerful Doctor in the World? 5 Top Contenders

10 Types of Drugs Used for Medicinal (and Illicit) Purposes

15 Types of Doctors With Different Specialties
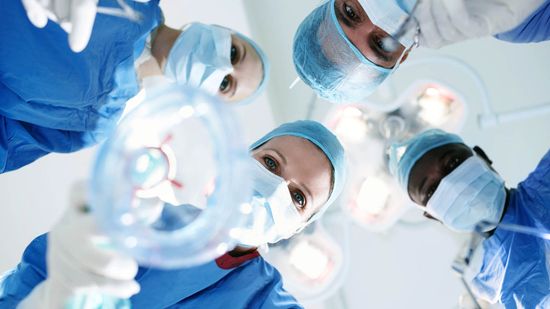
Anesthesia Awareness: When You're 'Awake and Aware' During Surgery

Prehab Could Make Your Recovery From Surgery a Bit Easier

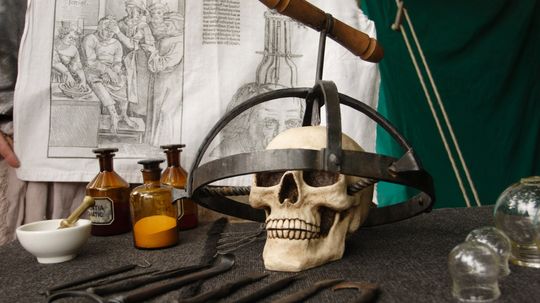
You Need It Like a Hole in the Head: The Ancient Medical Art of Trepanation

Honey Can Help If Your Child Swallows a Button Battery

What Is the Rarest Personality Type?
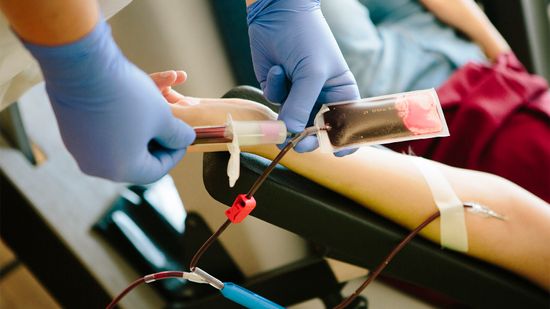
Veins, Needles, Yikes: What to Know Before Having Blood Drawn
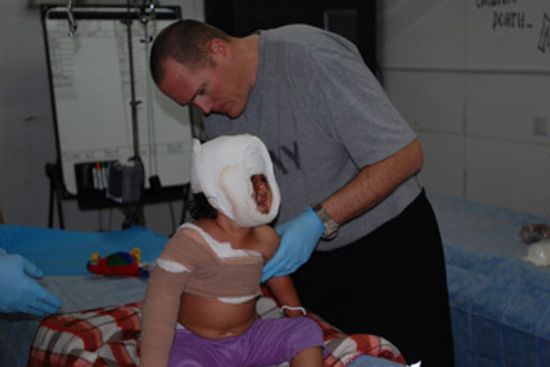
Are Army medics and doctors on the front lines?
Can civilians become doctors in the U.S. Army?

Do Army doctors and medics carry weapons?
Learn More
When people think of powerful professions, medicine usually tops the list. But who is the most powerful doctor in the world?
In the 1950s and 60s, a drug called thalidomide was marketed as a miracle solution for morning sickness and sleep issues in pregnant women.
Drugs can heal, harm or alter how the body works, depending on the type and how they’re used. Some are essential medicines that relieve pain or treat mental health issues. Others are addictive substances tied to recreational drug use and drug abuse.
Advertisement
Choosing the right physician starts with understanding the many types of doctors available. From primary care doctors to highly focused medical specialties, these professionals diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions.
The FDA's greenlighting of over-the-counter naloxone means that it will be available for purchase without a prescription at more than 60,000 pharmacies nationwide.
Doctors need to cut open dead bodies to learn anatomy, but where do they get them?
The billionaire business owner launched an online pharmacy in March with drug prices slashed. But is the model poised to disrupt America's prescription drug business?
By Dave Roos
Advertisement
Demand for potassium iodide pills has surged since Russia attacked Ukraine and threats of nuclear war loom. But why these pills, and what do they have to do with nuclear radiation?
It all comes down to the type of medicine, how much is required, and how quickly it needs to be absorbed.
Compression socks, sleeves and other garments are worn by both patients and athletes to help enhance their performance and improve their post-op recovery. But do they work?
It's rare, but when it happens, it can be traumatic and frightening for those who experience it. But how does such a thing even occur with today's modern medicine?
By Meg Sparwath
Advertisement
If your child swallows a button battery, you need to take them to hospital immediately. But on the way, grab your honey bear. Here's why.
By Dave Roos
Recovering from any surgery is never as easy as you hope. But putting in some time to get fit before it could make healing a lot easier. Here's how.
In the latest COVID-19 surge, many hospitals across the country are on diversion, meaning they're asking ambulances to take patients elsewhere. Here's how that could affect you.
Myers-Briggs has established 16 personality types and says that everyone fits into one of them. But some types are more common than others. Which is the rarest of all?
By Alia Hoyt
Advertisement
Drilling a hole in somebody's skull was all the rage 4,000 to 12,000 years ago. In fact, 5 to 10 percent of skulls from this period have a hole in them, made while the person was still alive. The question is, why?
Not crazy about going into your doctor's or therapist's office these days? You might be interested in a telemedicine service like Doctor on Demand.
Since the COVID-19 outbreak has people self-quarantining as much as possible, telemedicine has become a big alternative. But if you've never done it before, what can you expect?
By Alia Hoyt
A little girl with epilepsy caused the mash-up of a beloved children's book title and a CBD oil that changed medical history.
Advertisement
U.S. President Donald Trump has been touting the malaria drug chloroquine as a possible miracle drug for coronavirus. Should we all be taking chloroquine?
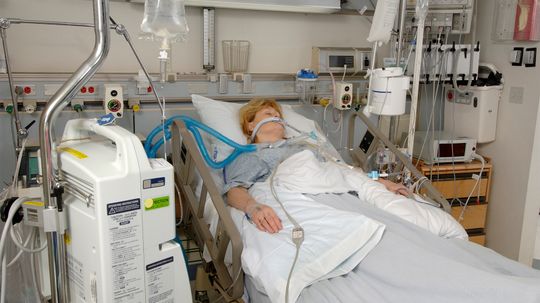
A ventilator is a machine that helps a person breathe by blowing oxygen into the lungs and removing carbon dioxide out of the lungs. They're a critical piece of equipment for coping with the COVID-19 pandemic.
Who do you call when there's a new disease outbreak? An epidemiologist. These disease detectives investigate the who, what, why, when and where of disease epidemics worldwide.
You've probably seen the ads for drugs to treat depression and the warnings that they may cause suicidal thoughts. But why would that be?
By Alia Hoyt
Advertisement
If you've got a pain in your head or body, you'll probably reach for whatever's in your medicine cabinet. But is it really the right treatment? One size doesn't fit all - we explain the differences in pain relievers.
By Alia Hoyt
Performing CPR on a woman means that, yes, there will be some hand-to-breast contact. Womanikin is designed to help reduce the stress and hesitation.