Medicine
Medicine has to do with diseases and conditions that affect the entire body. In this section, learn about testing and treatment plans including the medicines used to prevent and treat a range of diseases and conditions.

Is Your Hospital Diverting Ambulances Because of COVID-19?

How Ambulances Work

Can You Go to the ER Without Health Insurance?
Womanikin: Overcoming the Stigma of Breasts and CPR

Women Less Likely to Receive CPR in Public, Study Finds
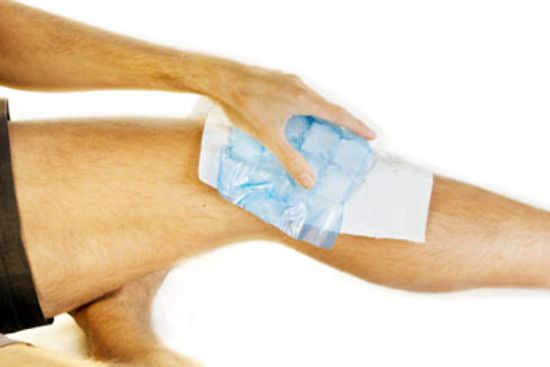
Should you use ice or heat to treat an injury?
Mark Cuban Wants to Solve the U.S. Prescription Drug Price Crisis

Epidemiologists Are the 'Disease Detectives' Protecting Public Health

Should Doctors Have to Pay Patients for Running Late?

Thalidomide: How a Miracle Medication Became a Global Tragedy

FDA Approves OTC Narcan Nasal Spray for Opioid Overdose

Why Are Potassium Iodide Pills Selling Like Crazy?

Who's the Most Powerful Doctor in the World? 5 Top Contenders

10 Types of Drugs Used for Medicinal (and Illicit) Purposes

15 Types of Doctors With Different Specialties
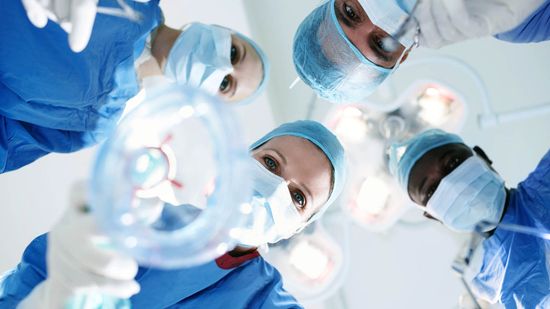
Anesthesia Awareness: When You're 'Awake and Aware' During Surgery

Prehab Could Make Your Recovery From Surgery a Bit Easier

You Need It Like a Hole in the Head: The Ancient Medical Art of Trepanation

Honey Can Help If Your Child Swallows a Button Battery

What Is the Rarest Personality Type?
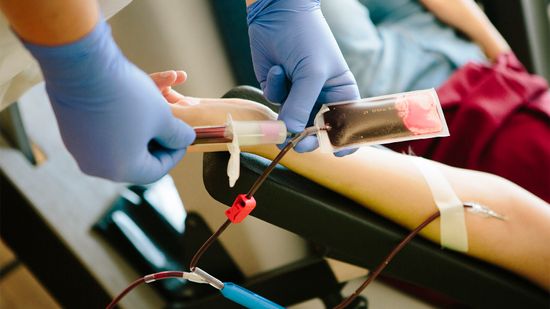
Veins, Needles, Yikes: What to Know Before Having Blood Drawn
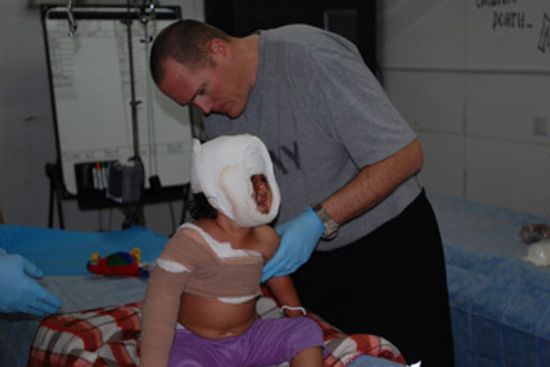
Are Army medics and doctors on the front lines?
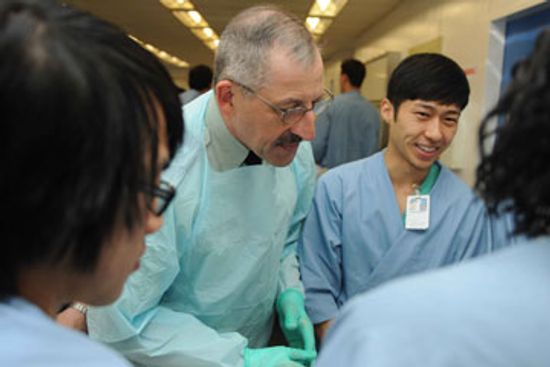
Can civilians become doctors in the U.S. Army?

Do Army doctors and medics carry weapons?
Learn More / Page 3
Docs are no different from the rest of us - they bring their unconscious biases into the workplace. But is there a way to lessen the impact of these biases on patients?
By Alia Hoyt
It may sound crazy initially - using a tooth to repair eyesight - but it's a very real surgery with a pretty impressive track record.
Bee stings hurt, so it seems like an odd proposition to get them on purpose. Believe it or not, the venom that makes that sting may also benefit humans in therapy.
Advertisement
You really liked that ER doctor who stitched up your arm. That is until you got your bill. Turns out the doctor was out of your insurance network, even though the hospital's ER is in network. How does that happen?
We all know a trip to the emergency room is never quick, but sometimes the ER is so jam-packed that you think that you're in the country's busiest ER. So just where is America's busiest ER? Well, it depends on who you ask.
You just broke your arm, and you're flat broke. But you don't worry about getting medical treatment, because the doctors and nurses in the ER have to treat everyone who walks through the door. Or do they?
Help! You just cut your hand while chopping vegetables. On the way to the hospital you cringe because you know that ER bill is going to be unbelievable. Why is that?
Advertisement
You've got health insurance. Congratulations! But good luck finding a primary care doctor. There are a lot fewer of them these days, so you may end up using that shiny, new insurance card in an emergency room.
We all know what to do in case of a medical emergency (get to the ER), but are you really qualified to recognize a true emergency when it happens?
You have to go to the ER, but you don't have health insurance. You're not worried, though, because emergency rooms have to treat everyone who walks through the doors. But does that mean you get out of paying the costs you incur?
Sometimes it's a lot easier to just take that expired cold medicine than run out to the drugstore when you're feeling sick. But are those expired meds even working? Or, worse, are they causing you harm?
Advertisement
There's an assortment of medications on the market to treat depression. But many of them are also effective for managing other health issues.
Salamanders regrow their tails. Starfish can grow new arms. When is it our turn? Let's take a look at what science has in the works.
Microorganisms aren't all bad. Can we fight fire with fire and pit good bacteria against the bad ones? Yes, but maybe not the way you think.
It can be hard to tell whether an injury, illness or other troubling symptom warrants a trip to the ER. While you should always err on the side of caution and go if you're unsure, these tips will make your decision easier.
Advertisement
Working in the ER isn't easy, and emergency medical professionals deserve a ton of credit for doing excellent work in less-than-stellar circumstances. But inevitably, sometimes things go wrong. And when they do, what legal options do you have?
Doomsday preppers recommend stocking up for the collapse of civilization -- and that includes antibiotics. But if you're getting them without a prescription, you're getting the veterinary kind.
When you're sick, sleep is one of the best things you can do to get better. But when you're several days into your antibiotics and still dragging, what's the cause: your illness or its cure?
Once you've gotten a sunburn during a course of antibiotics, you'll never forget the SPF again. But why would they lead to a burn in the first place?
Advertisement
Antibiotics are great at curing infections. But some are also great at upsetting your stomach and causing diarrhea. Which ones do we need to watch out for?
With some infections, it's hard to tell what may be causing your illness. And if it's serious, there's no time to wait for test results. Enter the broad-spectrum antibiotic -- and the problems it brings with it.
Humans tend to be forgetful when it comes to things that don't really interest us. Where did we put our keys? Did we take that last dose of antibiotics? We don't know about your keys, but we can help you with the penicillin question.
Antibiotics save lives. But broad-spectrum antibiotics can really do a number on the delicate ecosystem in your intestines -- and the recovery time may surprise you.
Advertisement
Robotic surgery doesn't mean Rosie from "The Jetsons" is going to get it. Instead, these high-tech bots let surgeons make the tiniest, most precise movements to limit tissue damage. But even now, researchers are dreaming up better robot inventions.
Family medicine isn't just for kids and their parents. The idea is that a physician sticks with you from birth to death, treating your whole body throughout your whole life. And it's changing with the times.